Glossary of telehealth terms
I drafted this glossary as part of my internship with the World Health Organization Regional Office for Europe. There, I was working on the topics of eHealth and the Global Network of Age-Friendly Cities (and trying to bridge the two). Much of this material, I first gathered when I was teaching a Master’s Engineering course on Telemedicine Techniques and Aspects for Aalborg University Department of Electronic Systems in 2010.
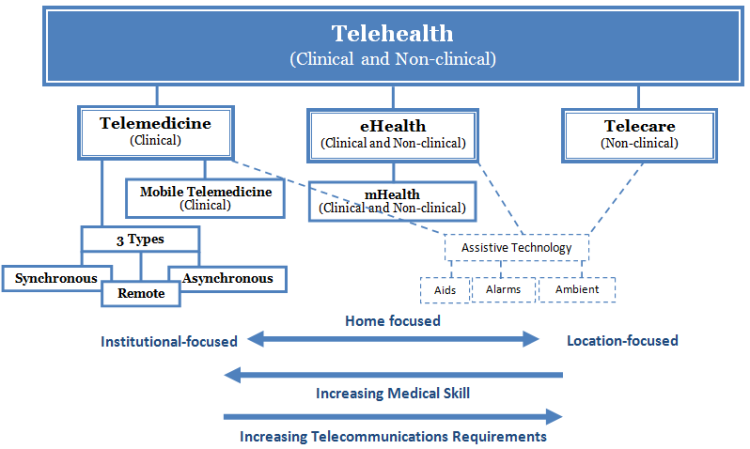
Telehealth consists of clinical and non-clinical health services that are provided from a distance and do not require the physical presence of the medical professional, student, or the citizen.
- Examples:medical education and research, administration, clinical procedures
o The umbrella term for health and medical knowledge sharing, encompassing telemedicine, telecare, eHealth, mHealth, health systems management, surveillance, health promotion, provides access to health and medical literature and public health functions and most other related concepts related to health and medicine practiced over a distance.
o The fundamental nature is in removing the constraints of time and distance to the delivery of medicalinformation and services.
Telemedicine is the clinical use of telehealth services that are provided over a distance
- Examples:teleconsultation viewing of patient files and images, teledisciplines such as telepsychiatry and teleradiology
3 types of telemedicine:
- Synchronous (real-time and interactive) – Telemedicine services that provide real-time interactions between patient and provider (i.e. phone conversations, online communication, virtual appointments)
- Asynchronous (store-and-forward) – Telemedicine services that involve acquiring and then transmitting medical data for assessment at a convenient time (i.e. sending images or patient information)
- Remote monitoring (self-monitoring) – telemedicine that enables medical professionals to remotely monitor a patient remotely by collecting and sending data (i.e. heart or respiration rate, blood-glucose levels)
Mobile Telemedicine – (a subdivision of Telemedicine) is clinical health provision from a distance through mobile systems
- Examples:portable defibrillators or temporary stations used in disaster response
Telecare – (a subdivision of Telehealth) is the provision of care from a distance provided as non-clinical services
- Examples:monitoring disabled, frail or aged persons, chronic condition management
eHealth is a method of telehealth for the use and transfer of health resources and care by electronic means, largely through ICT. It encompasses three main areas:
- The delivery of health information for health professionals and health consumers through the Internet and ICT.
- The use of e-commerce and e-business practices in health systems management.
- Using ICT and e-commerce to improve public health services.
- Examples:email with patients, electronic patient records, health information websites
mHealth – (a subdivision of eHealth) is electronic health provision or information through mobile communications devices. When relocated to provide direct medical care, such as with disease outbreaks, it is a subdivision of Mobile Telemedicine
- Examples:SMS medication reminders, PDA, mobile phone or other mobile device
Ambient Assisted Living includes devices, services and systems that provide unobtrusive support for daily living in the surrounding environment and based on the context, situation and the individual utilizing the assistance. It uses (intelligent) technologies to adapt the environment to the intra- and inter-user fluctuations.
It is noted that telehealth strives to improve the efficient use of health resources. Access to and use of the required ICTs is a primary hindrance for access to eHealth, particularly in rural, mountainous and lower income areas (i.e. digital divide). Likewise, a common clinical nomenclature is an issue in the use of telehealth, particularly across languages and cultures.
Pingback: WHO internship report | Doctor Dementia and the Dementia Adventure